In order to generate a more inclusive dataset of Pseudomonas genes mapped to putative in-paralogs and putative orthologs in other Pseudomonas species/strains, we developed a Pseudomonas Orthologous Groups classification system.
To generate ortholog groups, pair-wise DIAMOND searches were run on all genomes in the database to find reciprocal best hits (RBHs) for each gene. These analyses often resulted in multiple candidate genes for RBH status, which were narrowed down by examining the similarity between the query's flanking genes and the hit's flanking genes. If two candidate genes were directly adjacent, they where both accepted as RBHs that involve putative in-parology.
Pairwise intra-genome DIAMOND searches were also performed to acquire in-paralog information (i.e. gene duplications occurring after species divergence). If two genes in one genome were reciprocally more similar to each other than to any gene in the other genomes, the two genes were designated putative in-paralogs. Ortholog groups are built by starting with a seed gene and then adding all genes to which there is a RBH or in-paralog relationship.
Every new gene added to an ortholog group was then treated as a seed gene and the addition process was repeated until all qualifying genes had been added. The result was the development of orthologous groups, specifically generated for Pseudomonas species genomes, which can be used to sort search results.
Pseudomonas Ortholog Group POG000236
| Strain | Locus Tag | Description | Same-Strain Members | Fragment ? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH050 | V551_02171 |
hypothetical protein
|
3 same-strain members: V551_00857 V551_02171 V551_03687 |
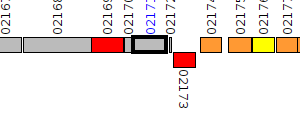
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH050 | V551_03687 |
oxidoreductase
|
3 same-strain members: V551_00857 V551_02171 V551_03687 |
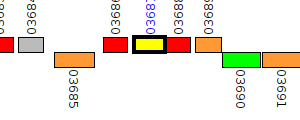
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH051 | V552_00875 |
oxidoreductase
|
3 same-strain members: V552_00875 V552_04085 V552_04878 |
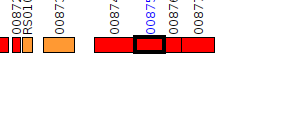
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH051 | V552_04085 |
oxidoreductase
|
3 same-strain members: V552_00875 V552_04085 V552_04878 |
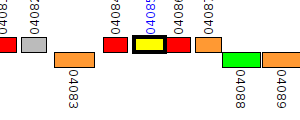
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH051 | V552_04878 |
oxidoreductase
|
3 same-strain members: V552_00875 V552_04085 V552_04878 |

|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH052 | V553_04384 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V553_04384 V553_04882 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH052 | V553_04882 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V553_04384 V553_04882 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH053 | V554_04763 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V554_04763 V554_05456 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH053 | V554_05456 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V554_04763 V554_05456 |
|
|
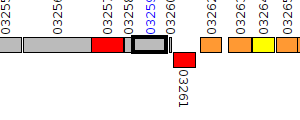
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH054 | V555_03259 |
dehydrogenase
|
2 same-strain members: V555_03259 V555_04544 |
|
|
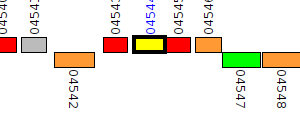
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH054 | V555_04544 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V555_03259 V555_04544 |
|
|
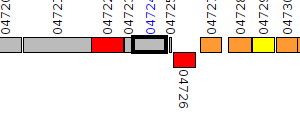
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH055 | V556_04724 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V556_04724 V556_05416 |
|
|
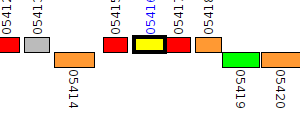
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH055 | V556_05416 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V556_04724 V556_05416 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH056 | V557_03775 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V557_03212 V557_03775 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH056 | V557_03212 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V557_03212 V557_03775 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH057 | V558_03881 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V558_03881 V558_04861 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH057 | V558_04861 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V558_03881 V558_04861 |
|
|
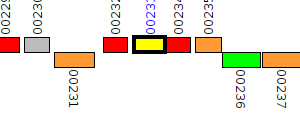
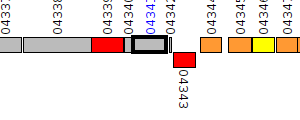
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH058 | V559_00233 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V559_00233 V559_04341 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH058 | V559_04341 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V559_00233 V559_04341 |
|
|
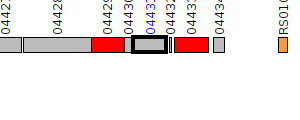
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BWH059 | V560_04431 |
oxidoreductase
|
2 same-strain members: V560_04431 V560_04903 |
|