In order to generate a more inclusive dataset of Pseudomonas genes mapped to putative in-paralogs and putative orthologs in other Pseudomonas species/strains, we developed a Pseudomonas Orthologous Groups classification system.
To generate ortholog groups, pair-wise DIAMOND searches were run on all genomes in the database to find reciprocal best hits (RBHs) for each gene. These analyses often resulted in multiple candidate genes for RBH status, which were narrowed down by examining the similarity between the query's flanking genes and the hit's flanking genes. If two candidate genes were directly adjacent, they where both accepted as RBHs that involve putative in-parology.
Pairwise intra-genome DIAMOND searches were also performed to acquire in-paralog information (i.e. gene duplications occurring after species divergence). If two genes in one genome were reciprocally more similar to each other than to any gene in the other genomes, the two genes were designated putative in-paralogs. Ortholog groups are built by starting with a seed gene and then adding all genes to which there is a RBH or in-paralog relationship.
Every new gene added to an ortholog group was then treated as a seed gene and the addition process was repeated until all qualifying genes had been added. The result was the development of orthologous groups, specifically generated for Pseudomonas species genomes, which can be used to sort search results.
Pseudomonas Ortholog Group POG000432
| Strain | Locus Tag | Description | Same-Strain Members | Fragment ? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa AZPAE15065 | NT81_RS09030 |
dihydroorotase
|
2 same-strain members: NT81_RS04370 NT81_RS09030 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa B136-33 | G655_02245 |
phenylhydantoinase
|
2 same-strain members: G655_02245 G655_29120 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa B136-33 | G655_29120 |
dihydroorotase
|
2 same-strain members: G655_02245 G655_29120 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL01 | Q055_00410 |
phenylhydantoinase
|
2 same-strain members: Q055_00410 Q055_05831 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL01 | Q055_05831 |
dihydroorotase
|
2 same-strain members: Q055_00410 Q055_05831 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL02 | Q056_03213 |
dihydroorotase
|
2 same-strain members: Q056_03213 Q056_04426 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL02 | Q056_04426 |
D-hydantoinase/dihydropyrimidinase
|
2 same-strain members: Q056_03213 Q056_04426 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL03 | Q057_02543 |
phenylhydantoinase
|
2 same-strain members: Q057_02543 Q057_04513 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL03 | Q057_04513 |
dihydroorotase
|
2 same-strain members: Q057_02543 Q057_04513 |
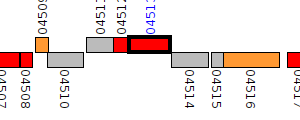
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL04 | Q058_04566 |
dihydroorotase
|
2 same-strain members: Q058_04566 Q058_05008 |
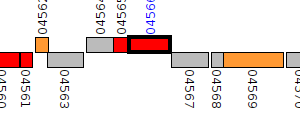
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL04 | Q058_05008 |
phenylhydantoinase
|
2 same-strain members: Q058_04566 Q058_05008 |
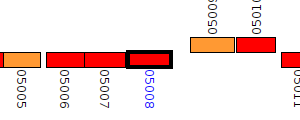
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL05 | Q059_05402 |
phenylhydantoinase
|
2 same-strain members: Q059_05155 Q059_05402 |
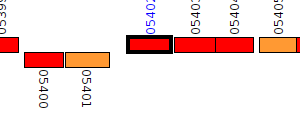
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL05 | Q059_05155 |
dihydroorotase
|
2 same-strain members: Q059_05155 Q059_05402 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL06 | Q060_04597 |
phenylhydantoinase
|
2 same-strain members: Q060_04597 Q060_03353 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL06 | Q060_03353 |
dihydroorotase
|
2 same-strain members: Q060_04597 Q060_03353 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL07 | Q061_03777 |
phenylhydantoinase
|
2 same-strain members: Q061_03777 Q061_05312 |

|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL07 | Q061_05312 |
dihydroorotase
|
2 same-strain members: Q061_03777 Q061_05312 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL08 | Q062_00479 |
phenylhydantoinase
|
2 same-strain members: Q062_00479 Q062_06363 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL08 | Q062_06363 |
dihydroorotase
|
2 same-strain members: Q062_00479 Q062_06363 |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa BL09 | Q063_02538 |
phenylhydantoinase
|
2 same-strain members: Q063_02538 Q063_03988 |
|